Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
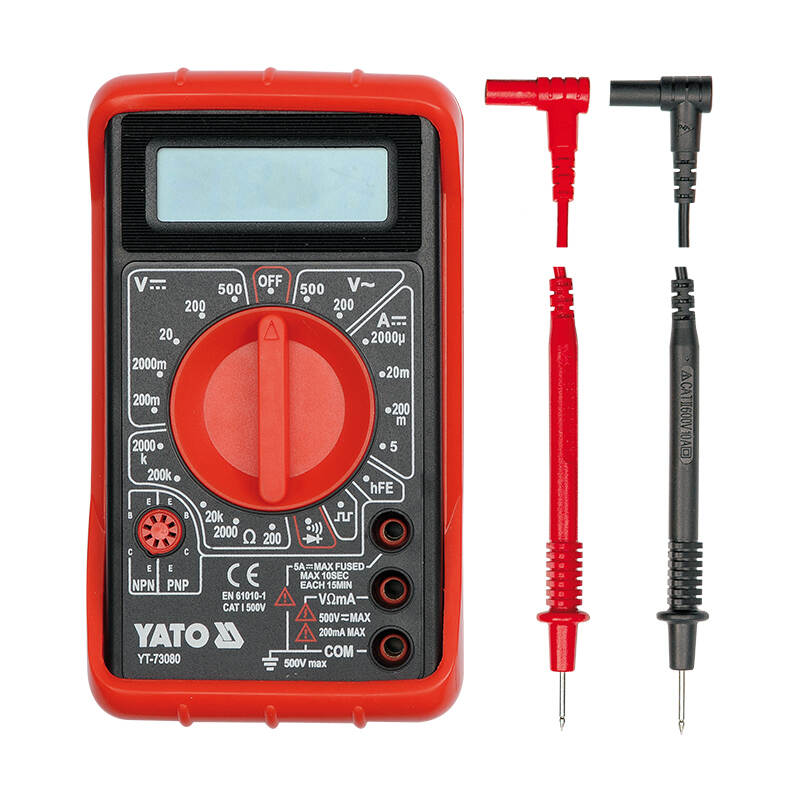







A digital multimeter (DMM) is an electronic testing device used to measure various electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and resistance. It provides accurate readings and is widely used by electricians, engineers, and hobbyists for troubleshooting and repairing electrical circuits. DMMs can also have additional features like measuring frequency, capacitance, and temperature, making them versatile tools for both professional and DIY applications. With a digital display, they are easy to read and interpret, simplifying the measurement process.
- Measurement Functions: Measures voltage (AC and DC), current (AC and DC), resistance, and often additional parameters like capacitance, frequency, and temperature.
- Digital Display: Provides clear and accurate readings on an LCD or LED display, making it easy to interpret measurements.
- Accuracy: Generally offers higher precision compared to analog multimeters, with varying levels of accuracy based on the model.
- Auto-Ranging: Many digital multimeters have an auto-ranging feature that automatically selects the appropriate measurement range, simplifying usage for the user.
- Data Hold Function: Allows users to freeze the displayed measurement for easier reading and recording.
- Backlight and Lighted Display: Some models come with a backlit display for better visibility in low-light conditions.
- Additional Features: May include features like continuity testing, diode testing, and data logging capabilities.
- Portability: Compact and lightweight design, making it easy to carry and use in various locations.
- Safety Ratings: Often designed with safety features, including fuses and overvoltage protection, which are critical for user safety during electrical testing.
- Battery-Powered: Typically powered by batteries, ensuring they are versatile for use in both fieldwork and workshops.
- Electrical Diagnostics: Used by electricians to troubleshoot electrical circuits, identify faults, and ensure proper functioning of electrical systems.
- Home Appliance Repair: Handy for technicians to test and repair home appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves.
- Automotive Testing: Employed in automotive diagnostics to measure battery voltage, check alternator output, and diagnose electrical issues in vehicles.
- Electronics Development: Used by engineers and hobbyists in the design, testing, and debugging of electronic circuits and devices.
- HVAC Systems: Essential for HVAC technicians to measure and troubleshoot heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Industrial Maintenance: Widely used in industrial settings for maintaining and inspecting machinery and equipment to ensure operational efficiency.
- Renewable Energy: Useful for solar panel installations and maintenance, allowing for the measurement of voltage output and performance verification.
- Laboratory Experiments: Employed in educational laboratory settings for experiments involving electrical measurements and principles.
- Fieldwork: A vital tool for field technicians in different industries (telecommunications, utilities, etc.) for on-site testing and verification.
- Safety Testing: Used to ensure electrical systems comply with safety regulations by measuring insulation resistance and performing continuity tests.






