Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
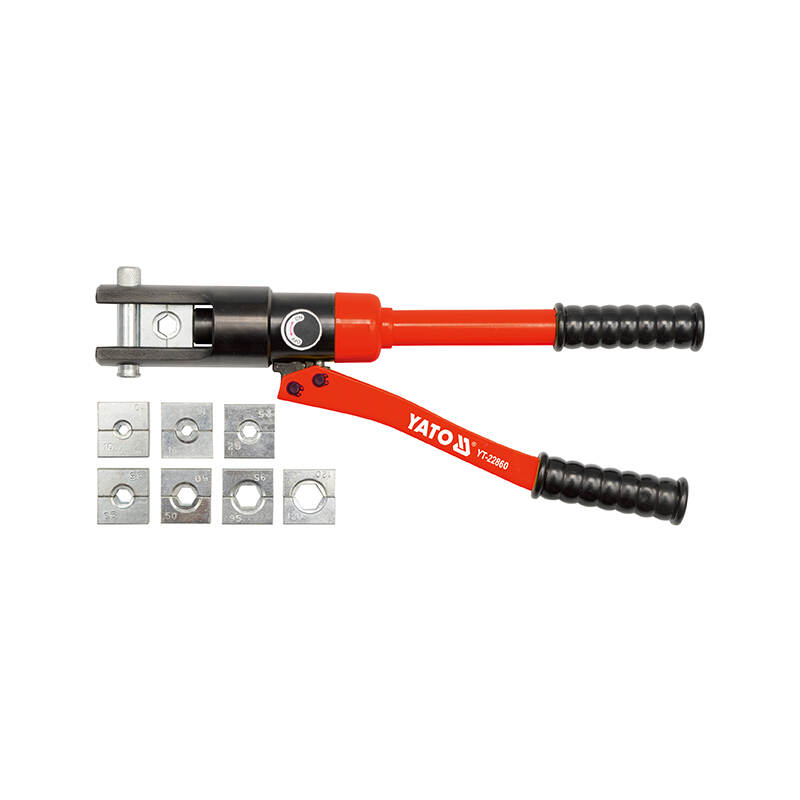




Hydraulic pliers are specialized tools that use hydraulic pressure to amplify force, making it easier to grip, cut, or bend materials. They typically feature a handle that, when squeezed, activates a hydraulic mechanism inside, providing significant power without requiring much effort from the user. These pliers are commonly used in various applications, including construction, automotive repair, and electrical work, due to their efficiency and effectiveness in handling tough tasks.
Hydraulic Pliers
The Features
1. Hydraulic Mechanism: Utilizes hydraulic pressure to increase gripping and cutting power, making tasks easier and requiring less manual effort.
2. Versatile Application: Suitable for various industries, including construction, automotive, and electrical work, allowing for a wide range of uses.
3. Ergonomic Design: Often designed with comfortable handles to reduce user fatigue during prolonged use, enhancing overall usability.
4. Durability: Made from high-quality materials, hydraulic pliers are built to withstand heavy use and resist wear and tear over time.
5. Precision: Provides precise control and force application, making it ideal for delicate tasks as well as heavy-duty operations.
6. Safety Features: Many models include safety locks and features to prevent accidental activation, ensuring safe operation.
7. Compact Size: Despite their power, many hydraulic pliers are compact and portable, making them easy to carry and store.
Application Area
1. Automotive Repair: Used to grip, cut, or bend various automotive components such as wires, pipes, and clamps, making repairs easier and more efficient.
2. Construction: Ideal for tasks like fastening rebar, cutting metal rods, or bending metal sheets on construction sites, enhancing productivity.
3. Electrical Work: Employed for stripping wires or connecting and disconnecting electrical components securely, ensuring safety and accuracy.
4. Plumbing: Useful for gripping and cutting pipes, as well as connecting fittings with precision, facilitating plumbing installation and repairs.
5. Metalworking: Applied in metal fabrication to manipulate and shape metals, including cutting and bending operations, which require significant force.
6. Rescue Operations: Utilized in emergency response situations, such as extricating individuals from vehicles or collapsed structures, thanks to their powerful cutting capabilities.
7. Maintenance and Repair: Commonly used in maintenance tasks across various industries for general repairs and adjustments where high force is needed.



